Feudatory States in Madhya Pradesh
Introduction Madhya Pradesh had always been a state of riyasats were people were not directly ruled by some large kings. The state used to be divided in small states which were called feudatory states. These feudal were managed by Jagirdars.
These Jagirdar used to report to their higher management namely kings or British. Main function of these Jagirdarwas to collect revenue and share it with higher statesman.
Madhya Pradesh of 1951 was a composite state. The all-inclusive community of the eight Marathi talking districts.Madhya Pradesh is the heartland of the nation.
1956, in the midst of the patching up of states in India on the phonetic commence. It is involved five region ns to be particular, Madhya Bharat, Vindhya Pradesh, Bhopal, Sironj sub division of Vidisha range and Mahakoshal. Before opportunity, Madhya Bharat, Vindhya Pradesh and Bhopal were separate states while Sironj sub division of Vidisha region was the bit of past Rajasthan.
The merger of the Vindhya Pradesh into Madhya Pradesh is noteworthy. VP involved the domains and ranges surrounding the present day region of Datia, Chhatarpur, Tikamgarh, Panna, Satna, Damoh and Rewa. Molded as a grouping “C” state, it mechanically went up against issues of sustenance lack and nonappearance of advantages even to run the state association.
Along these lines, it was finally met into MP. The predetermination of VP was a persuading power behind the merger of the regions of (Surguja, Korea and ChhangBhakor) and (Raigarh, Sakti, Jashpur and Udaipur), which in like manner contained modestly more prosperous Chhatisgarh area, into the territory of M.P.
Status of Feudatory States in Madhya Pradesh
The total number of feudatory states 116 in the district of the Madhya Pradesh. The two associations Bundelkkhand and Banghelkhand in the central province controlled35 state. In Bundelkhand there were 15 communicates each having a zone of under 50 square miles.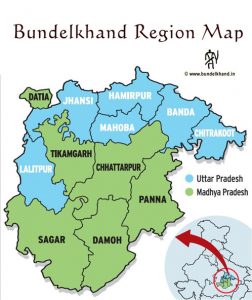
There were 15 little Rajput state and four muslim states in the Malwa district of the Madhya Pradesh paying tributes to the rajas of Indore and Gwalior. Once the English had taken the principles under their wings, they ceased to pay tributes to their current over-loads. Dhar and Devas were two driving states of the malwa region.
In the baghelkahnd office procured to nearness in March, 1871.
Rewa was the biggest t which was measured 12000 square miles. Of the feudatory states Baster was the greatest having a region of 39,060 sq. km, 205 sq. km more than the scope of present Kerala which is 38,855 sq. km.
Madhya Pradesh government under Dwarka Prasad Mishra dispatched a gigantic police energy to Baster on walk 25, 1966 which tore open the portal of the regal home of the past baster ruler PravinchandroBhanjdeo and shot him dead nearby more than 200 tribes who were testing the treatment apportioned to him after his state baster was united.
Famous Jagirs
Madhya Pradesh had many small and large Jagirdars in its state. We will discuss about these here.
The ChaubeJagirs, otherwise called ‘KalinjarChaubes’, jagir states were a gathering of five feudatory conditions of Central India amid the time of the British Raj. They were a British protectorate from 1823 to 1947 and had a place with the Bagelkhand Agency. Their last rulers joined the Indian Union in 1948.
Until the eighteenth century the first grounds of the family had been in Dadri, close Nowgong cantonment. Once under the administration of Raja Chhatrasal of Panna State the Chaubis achieved high positions. The proprietors of the initial four bequests were relatives of Ram Kishan, the previous legislative head of Kalinjar under Raja HirdeSah of Panna.
At the point when Ali Bahadur, the Nawab of Banda attacked Bundelkhand, Ram Kishan seized Kalinjar post. For a long time he opposed the endeavors of the Nawab to assume control over the fortification.
At the point when British run was built up in India, Kalinjar was administered by the children of Ram Kishan. They had been seven siblings, yet the eldest, Baldeo, had passed on and the most youthful child Daryau Singh was in summon. In 1812 the British government allowed them a sanad recognizing the ownership of the regions by Daryau Singh and his siblings.
Be that as it may, Daryau Singh contradicted the British and started to exasperate the peace, so that on 16 January 1812 Coronel Martindell assaulted Kalinjar stronghold. At last Daryau needed to arrange surrender under the condition that specific grounds would be given to his relatives in trades for those he possessed.
The condition was acknowledged by the British specialists;however the transactions were troublesome. Isolate sanads were issued, including one for Gopal Lai Kayasth, who had been the wakil of the family. In 1817 there were further disagreements.
In 1862 the Jagirdars were conceded a sanad of appropriation. The decide was that when there were no beneficiaries the home was part between alternate individuals. At first there were nine realms however in 1839 two were at that point smothered.
In 1855 one home was seized attributable to the ramifications of the ruler in a murder case. Additionally in 1864 another realm was smothered and consequently just five remained.
The Jagirs were under the Bundelkhand Agency of the Central India Agency until the point that 1896 when they were exchanged to the BaghelkhandAgency.In 1931 they were exchanged back to the Bundelkhand Agency.
The Bundelkhand Agency was limited by Bagelkand toward the east, the United Provinces toward the north, Lalitpur District toward the west, and the Central Provinces toward the south.
The Bagelkhand Agency was isolated from Bundelkhand in 1871. In 1900 it included 9 states, 13 homes and the pargana of Alampur having a place with Indore State. In 1931, the greater part of the Baghelkhand Agency states were exchanged back to Bundelkhand, with the exception of Rewa (title Maharaja, Hereditary salute of 17-firearms), which was set under the expert of the Indore Residency.